

Over time my dogs would become especially excited when I would bring out the running shoes. I always put on a special pair of running shoes prior to heading out for the jog. The meal preparation routine serves as a stimulus that predicts the meal which is biologically relevant.įor much of my life I enjoyed jogging and I would take a dog or two with me since they seemed to enjoy it at least as much as I did. In this case, they often drool just like Pavlov's dogs. With my dogs, I have a meal time ritual where I ask the dogs to sit for a moment or two while I prepare their meal. In some cases, it may even try to take you to the food bowl or bring the food bowl to you. When it comes that time of day, the dog may get restless. In this case, time serves as a stimulus that predicts the meal. There are structures in the brains of animals that regulate various circadian (about a day) rhythms. If you feed the dog at the same time(s) each day, the dog learns this. If you do this regularly, I bet the dog will get excited when you ask this question. Or, perhaps you are in the habit of asking the dog, " Do you want to go for a walk?" before you do so. That is, when the dog sees the leash, it will get excited and will orient to the door you typically exit from. As a result of the leash (a stimulus) predicting the walk (which I would argue is biologically relevant because of bathroom behaviors, etc.), the dog learns through Classical Conditioning.
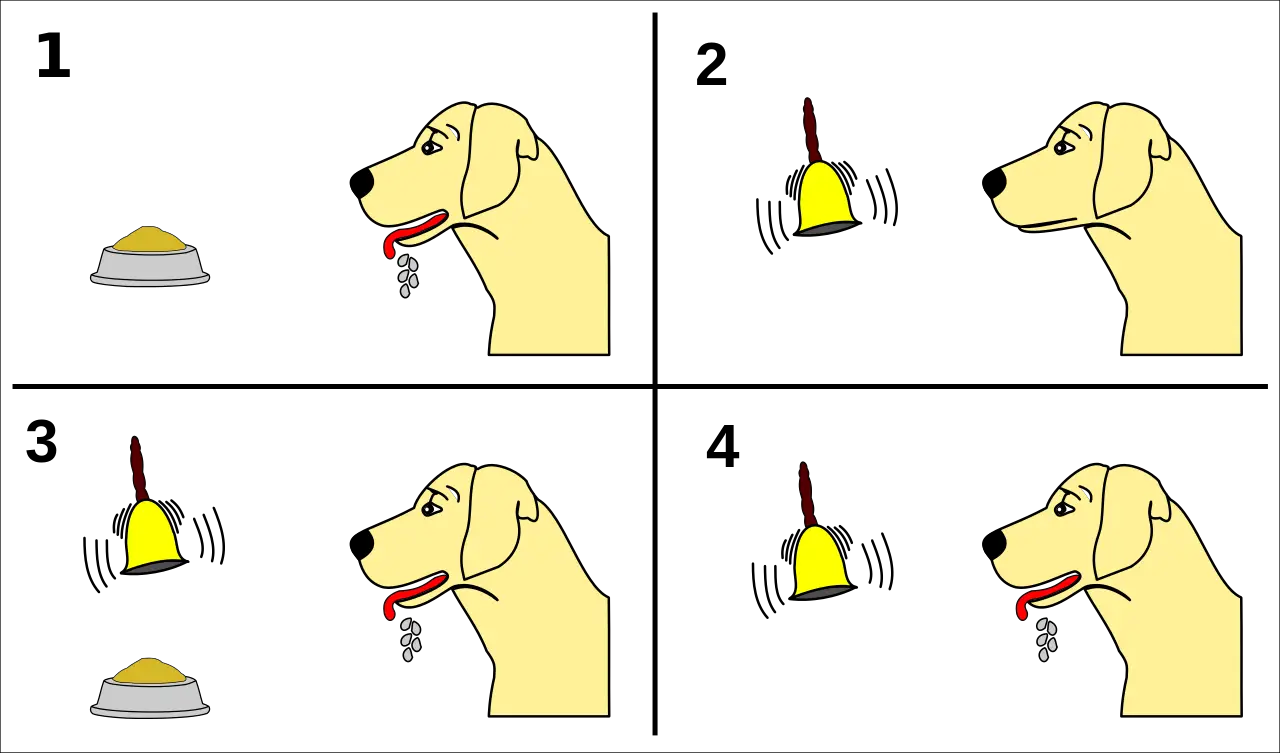
A lot of people that own dogs walk them with a leash. In this article, I hope to make clear that Classical Conditioning involves a lot more than just drooling dogs. Classical Conditioning is also called Pavlovian Conditioning and it often makes people think of drooling dogs. The salivating helped prepare the organism to receive the food. He found that if the sound of a tone (a stimulus or S) reliably predicted the occurrence of food (a biologically relevant stimulus or S*), the dog would learn to salivate to the tone. Ivan Pavlov was a Russian physiologist that discovered Classical Conditioning in the early 1900s. This learning enables the dog to prepare for the biologically relevant stimulus. To make a long story short, the dog learns " what predicts what". The asterisk indicates that the stimulus is biologically relevant (that is, "special"). The basic paradigm (or setup) is:Ī Stimulus predicts a biologically relevant Stimulus Thus, the purpose of this article is to provide the reader with a basic understanding of Classical Conditioning and how it relates to dog training and behavior.Ĭlassical Conditioning is concerned with events in the environment (called Stimuli) that predict the occurrence of biologically relevant events (or "special" Stimuli). Dog trainers don't talk about it as much, however, I believe that an understanding of it will lead to a better understanding of why our dogs do what they do as well as to more effective training. I have previously written articles about Operant Conditioning as well as its variations.Īnother type of conditioning (or learning) is called Classical Conditioning. That is, many trainers use reward (and perhaps punishment) as a way to modify a dog's behavior. For example, these days a lot of dog trainers are fairly well versed in Operant Conditioning. The scientific study of animal learning has provided a lot of useful information for dog trainers.
PAVLOV DOG HOW TO
As you might expect, I am interested in how to apply what science knows about animal learning and behavior to dog training. I am a scientist who studies animal learning and behavior and I am also a dog trainer. Learning What Predicts What: Pavlov and Dog Training


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
